Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) has now emerged as a fast spreading threat to human health. Unless detected early, damage to the kidney tissue in CKD is irreversible and progressive . New studies have shown that Diabetes , hypertension , drug abuse are closely linked to kidney disease .
 Inculcating healthy eating habits, and avoiding smoking and alcohol can reduce the risk of kidney disease.
Inculcating healthy eating habits, and avoiding smoking and alcohol can reduce the risk of kidney disease.
Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Origin (CKDU) has also baffled specialists in the field with regard to its origin.
The Sunday Observer spoke to an eminent nephrologist from the Sri Jayewardenepura General Hospital Dr Chinthana Galahitiyawa for more insights into the subject.
Excerpts ...
 Q. Chronic kidney diseases are now the hot topic of the day, with the President and Prime Minister both calling for urgent measures to be put in place to prevent its spread. Firstly, since most people still don’t know much about kidney disease, what exactly is chronic kidney disease?
Q. Chronic kidney diseases are now the hot topic of the day, with the President and Prime Minister both calling for urgent measures to be put in place to prevent its spread. Firstly, since most people still don’t know much about kidney disease, what exactly is chronic kidney disease?
A. Chronic kidney disease is the gradual loss of kidney function over a period of months or years. Damage to kidney tissue in CKD is irreversible and progressive even if the cause is eliminated. Causes may vary, and typically no symptoms in early disease.
Q. What is the role of the kidney and how is it linked to these diseases?
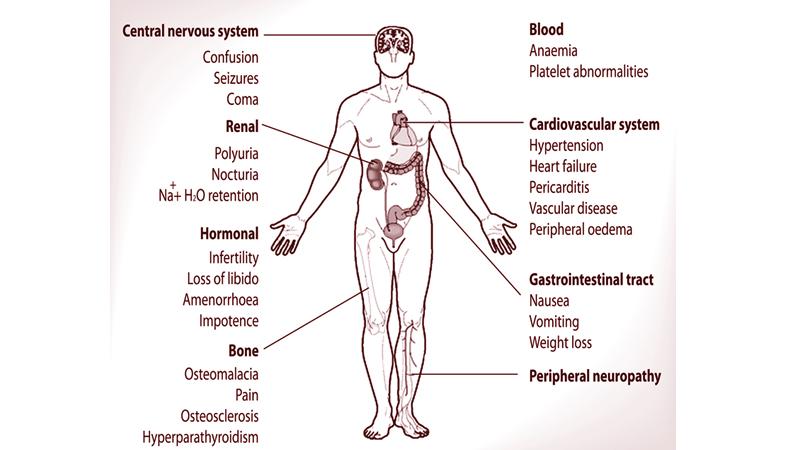
A. Kidneys have multiple functions essential for life. It regulates blood volume by controlling urine production. Blood pressure, ionic composition of blood and blood acid –base regulations are also done by the kidneys. Red blood cell production and vitamin D synthesis are supported. Further, excretion of waste products and foreign substances from the body is basically done by the kidneys.
In chronic kidney disease all of the above functions get impaired. This will lead to the variable symptoms experienced by the patients.
Due to failure of water excretion swelling of the body is seen. Here, commonly, the face and ankles are involved. In addition to the visible swelling, internal organs are also affected. This results in shortness of breath due to wet lungs.
High blood pressure is a feature of kidney failure as the regulation by the kidney is lost. Key ions in the body, including potassium, sodium and chloride are basically controlled and even a mild alteration of these will create an unfavourable environment for the body.
High potassium levels can cause heart rhythm disturbances, low sodium is associated with confusion and low calcium levels cause muscle weakness. Maintaining body’s acid-base proportions is essential to maintain cell functions optimally.
A hormone called erythropoietin is synthesisedby the kidney cells which stimulates bone marrow to produce red cells to maintain haemoglobin. Lack of this hormone results in anaemia. A key step in vitamin D synthesis happens in the kidney.
Q. How is it caused ? What are the trigger factors?
A. Causative factors of CKD are diverse. Pathways of damaging kidney cells may vary depending on the aetiology, but the end result is death of kidney cells and scarring. This is the reason why the damaged kidneys cannot be regenerated.
Q. Diabetes is now being cited as a link to CKD. Studies have found that diabetes accounts for 44% of new cases of CKD, in South Sri Lanka. Do you agree? ( explain in detail how diabetes increases the level of sero in blood vessels damaging kidney tissues etc and what happens thereafter.)
A. Diabetes is the number one cause of chronic Kidney disease anywhere in the world. When the prevalence of diabetes goes up, the number of CKD patients also goes up.
Elevated blood sugar levels damage the small blood vessels in the body. This affects many organs, kidneys, eye and nervous system.
The initial feature is mild protein leak in urine which can only be detected by special urine tests and missed in routine tests.
Then, it progresses to high leaking stage and is readily detected by simple urine tests.
At this stage the patients observe that their urine is more frothier now than before. Following this stage the kidney functions start to deteriorate gradually.
Poorly controlled blood sugar levels will expedite the damage and in patients with high blood pressure, deteriorate faster. Kidney damage in diabetes will be enhanced by recurrent infections in any part of the body, due to certain antibiotics used for them and painkillers.
Q. What are the adverse effects of chronic kidney disease on the human body?
A. Chronic kidney disease in children will impair the growth. CKD patients will experience the following problems: excessive water in the body causing swelling and shortness of breath, confusion and body weakness due to accumulation of toxic substances in the body, heart rhythm disturbances due to salt imbalances, uncontrollable high blood pressure, anaemia, skeletal problems due to low vitamin D and calcium levels.
Further, CKD patients will commonly experience loss of appetite, lack of sleep, body aches and pains, darkening of skin and body itch.
Q. Are they permanent? Or do these negative effects go away after some time? How?
A. Calcium and vitamin D can be supplemented and blood acidity can be neutralized by drugs. Erythopoetin hormone can be given in the form of injections to improve the haemoglobin. Lack of sleep, body itch and appetite can be helped with certain medicines.
But, these symptoms and problems cannot be treated completely with medicines.
The only way is to get the duties of kidneys done by some other way, such as, a kidney transplant. But, dialysis will do some of the tasks of the kidneys such as, cleaning of toxins from the blood and remove excess water from the body.
Q. How is chronic kidney disease diagnosed?
A. CKD is suspected when patients have one or more of the above symptoms. But, symptoms are usually late in CKD. In high risk patients screening will help to diagnose early and thereby improve the outcome.
Main tools in diagnosing CKD include urine tests, blood biochemistry for creatinine, urea and potassium, imaging of kidneys by ultrasound scanning. Complications of CKD is detected by many other directed urinary, biochemical and radiological investigations.
Q. Of the most damaging effects of chronic kidney disease, what comes to your mind?
A. Chronic ill health and debility caused by the illness is the main short term effect, but in the long term CKD increases one’s risk of early death.
Q. Can these negative effects be reversed? How?
A. Kidney transplant will normalize most of the ill effects caused by the CKD and reverse most of the negative effects of CKD patients.
Q . Can taking calcium supplements increase risk of kidney stones and thereafter lead to CKD?
A. Calcium is used in CKD not only to supplement calcium but also as a binder of excessive phosphates in diet. Calcium supplements can be associated with kidney stones if used excessively without monitoring the biochemistry.
Q. It has been said, over the counter drugs like too much painkillers can damage kidneys. Your comments?
A. Yes, strong painkillers that belong to the drug class called NSAID can damage kidneys permanently.
Q. What are the treatment options?
A. Dialysis is the basic treatment where toxins are removed mechanically from the body. Two types of dialysis is available i.e. Haemo dialysis and Peritoneal dialysis. In the former, the patient’s blood is cleaned by a machine twice or thrice a week at a dialysis centre. At each session it is carried out for 3 to 4 hours.
Peritoneal dialysis(PD) in contrast is basically done at home and is a continuous process. The best treatment for CKD is kidney transplant which gives the patients more freedom to lead a normal life.
Q. Chronic Kidney Diseases of an Unknown Origin ( CKDU ) has in recent years begun to baffle the local kidney experts as the disease is fast spreading, especially, in the south . There is still controversy over the exact reason even though the WHO has released a study saying drinking polluted water from tanks, rivers and wells was a primary cause. Your comments?
A. Still the exact causative agent of this unfortunate condition is not scientifically established. It’s likely to be entering the patients with drinking water and all polluted water should be avoided.
Q. What are the effects of this disease? How serious are they?
A. This group also has similar health issues due to kidney failure which cannot be differentiated from the others, once established. There are a few subtle changes seen in this group which involved the less prominent protein loss in urine, less prominent high blood pressure and slow progressive disease.
Q. What is end stage kidney disease? Does it require hospitalisation?
A. End stage kidney disease is irreversible complete impairment of kidney function which needs kidney replacement treatment to maintain life.
Scientifically, we can calculate the existing amount of kidney functions and when it is less than 10 can call end stage kidney disease (normal is 80-120).
Q. How can those affected by the disease be protected?
A. In addition to providing health care, all in this high risk geographical area should be provided with clean water for drinking and cooking purposes. This might help to minimize the entry of toxic substance into the body.
Q. What do you consider as being the most urgent need these vulnerable communities need at present?
A. CKD screening is done systematically by the Health Ministry and the positive cases are referred to tertiary care centres for specialized management. The recent emerging of a large number of cases over the last few years is mainly due to the detection of hidden cases by this community screening programs. These communities need health education on the value of clean water, ways of minimizing exposure to agrochemicals and the value of treatment with good compliance.
Q. What are the treatment options?
A. Treatment is basically similar to any CKD patient which we have discussed earlier. The only difference should be the prevention of further exposure.
Q. The golden rules to follow on dietary and lifestyle changes to reduce CKD and CKDU in Sri Lanka?
A. Diabetes and high blood pressure.. awareness and regular screening of high risk groups is a must. High risk groups include all diabetics, hypertensives, people who live in endemic areas of agricultural kidney disease, who have positive family history of CKD and people with any other kidney diseases, such as, kidney stones.
To maintain kidney health in general we should consume enough safe water, treat blood sugar and high blood pressure properly, avoid high salt in diet and over the counter medication. Stop smoking. Maintain a healthy weight and have an active lifestyle with regular physical exercises.
Q. Finally, what is the message you wish to impart to local patients on World Kidney Day?
A. This year’s theme is ‘kidneys and women’s health’. There are a few conditions which specifically affect women’s kidneys. These include, complications in pregnancy and autoimmune type of kidney diseases. Kidney infections are seen more frequently in females than in males. CKD reduces the fertility of women and also results in poor outcomes in pregnancy. Certain complications of pregnancy can lead to CKD and timely diagnosis and management of these can prevent permanent damage. Public awareness, prevention, early detection and timely treatment are the factors to promote women’s kidney health.
